Describe the Relationship of an Estuary and the Tide
Mixing In a well-mixed estuary lines representing constant salinity move ________ during low tides or periods of high river flow and they move ______ during high. Estuaries are areas where runoff and tide interact.

1 A Tide Dominated Estuary Ideal Distribution Of Sedimentary Bodies Download Scientific Diagram
Describe the distribution of salinity values in a typical estuary from surface to sediment and from head to mouth.

. When dense salty seawater flows into an estuary it has an estuarine current. During low tide or when river runoff levels are high due to rain or snow melt estuaries will have more freshwater and therefore lower salinity. Plants and animals that can tolerate only slight changes in salinity are called stenohaline.
In the calmer middle and upper reaches of an estuary where the river and the tidal currents meet especially in the slack water at high tides also the mud can be deposited. Tides create the largest flow of saltwater while river mouths create the largest flow of freshwater. A tide is a necessary force to.
Describe the pattern of water circulation in a typical estuary as the tide changes. For example tides at the end of a long narrow inlet might be amplified because a large volume of water is being forced into a very small space. Finding the Salt Front-Students watch a video then use Hudson River salinity data to find the location of the salt front and observe patterns of change in salinity along the estuary.
Compare and contrast the type of sediment found at the head of an estuary as opposed to its mouth. Once or twice a day high tides create saltwater currents that move seawater up into the estuary. Influence of Tides Like other coastal communities estuaries are dramatically influenced by tides.
To survive in these conditions plants and animals living in estuaries must be able to respond quickly to drastic changes in salinity. They are generally located in areas where the tides are wide with beaches to the sides that when they go away exhibit their flora. An estuary may also be called a bay lagoon sound or slough.
During the day time when the tide is out many aquatic creatures retreat into protective postures. The key feature of an estuary is that it is a mixing place for sea water and fresh water to supply fresh water. The transition of an estuary to different morphologic states may be explained in part by the relationship of tidal asymmetry to net sediment transport.
In a partially mixed estuary the vigorous rise and fall of the tide generates strong turbulence and causes partial mixing between the fresh water above and the salt water below. Describe the factors that result in this. Tides Reading The Hudsons Ups and Downs Student Activity Teacher Section Tides and Water Levels Extension.
Under these conditions the river flow entrains 10 to 20 or more times its own volume of salt water and the compensatory landward flow of seawater near the bottom is correspondingly increased. The estuarine tidal flood current and tidal level decrease with the increase in river discharge and distance from the river mouth. One consistent feature in estuaries is their fluctuation in salinity.
Organisms that live in estuaries must be adapted to these dynamic environments where there are variations in water chemistry including salinity as well as physical changes like the rise and fall of tides. Since many other similar relationships have been suggested. Tidal waves propagate upstream from river mouths and produce tidal currents and tidal level variations along rivers.
The friction and the non-linear transfer of energy strongly delayed. A tidal cycle of two high tides and two low tides each lunar day with the high tides of nearly equal height. Tide-dominated estuaries are composed by sediments that derive from both fluvial and offshore sources and the grain size varies from gravel to mud.
Proposed the simple relationship A 1000Ω085 to describe the relationship between cross-section area and tidal prism of a tidal inlet on inlets of the west coast of the USA based on an empirical data analysis. The strength of tidal currents the rate of freshwater added the bottom topography and the depth of the estuary all affect the vertical _____ and stratification in an estuary. Low tides also once or twice a day reverse these currents.
Introduction to Tides Lesson 4. In almost all estuaries the salinity of the water changes constantly over the tidal cycle. High tides can create estuarine currents.
Water continually circulates into and out of an estuary. Clams can close their shells worms stay underground while other creatures sleep. During high tide or drier seasons such as the summer in North America an estuary will have more salt water and increased evaporation and therefore higher salinity.
An estuary is the part in which the watercourses that go to the ocean flow. An estuary reaches an equilibrium state when the quantity of sediment transported during flood tide is balanced by the quantity of sediment transported during ebb Dyer 1997. The tidal pattern in an estuary depends on its geographic location the shape of the coastline and ocean floor the depth of the water local winds and any restrictions to water flow.
So cold water is more denser then warm water until the cold water freezes into ice. Cold water is more dense then warm water because the cooler something gets the more dense it gets. The amount of matter in a given space.
Unlike other temperate estuaries the average tidal range in the PRE increases gradually from the offshore region to the estuary reaching a maximum at the head of the PRE Humen as the estuary becomes narrower and shallower which concentrates the energy of the tides Xu 1985. Estuaries are areas of water and shoreline where rivers meet the ocean or another large body of water such as one of the Great Lakes. Water movements in estuaries transport organisms circulate nutrients and oxygen and transport sediments and wastes.

Typical Morphology Of Wave Dominated Estuaries After Dalrymple Et Al Download Scientific Diagram

Estuaries Where The River Meets The Sea Learn Science At Scitable
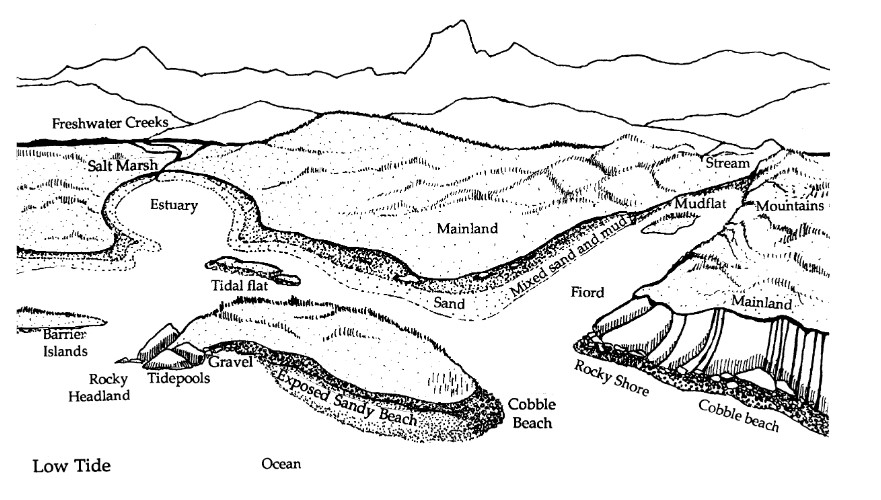
Estuary Investigations Oregon Sea Grant Oregon State University
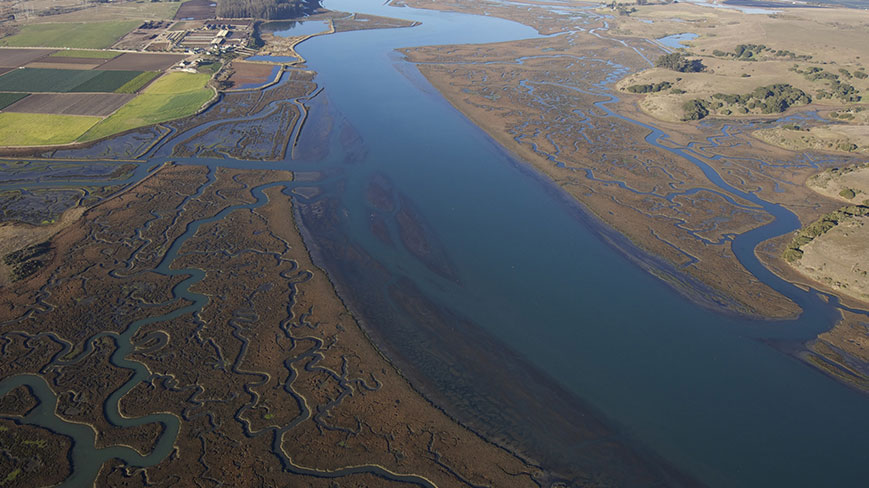

What Is An Estuary Estuaries Tutorial

Tidal Range An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
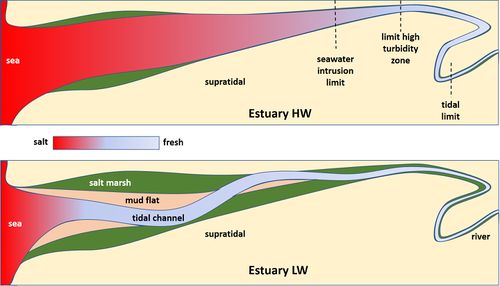
Estuarine Ecosystems Marinespecies Introduced Traits Wiki

Estuary An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

1 A Tide Dominated Estuary Ideal Distribution Of Sedimentary Bodies Download Scientific Diagram
Tidal Asymmetry And Tidal Basin Morphodynamics Coastal Wiki

Typical Morphology Of Tide Dominated Estuaries After Dalrymple Et Al Download Scientific Diagram
Tidal Asymmetry And Tidal Basin Morphodynamics Coastal Wiki

Morphology Of Estuaries Marinespecies Introduced Traits Wiki

Estuary Coastal Feature Britannica

Physical Processes And Morphology Of Synchronous Estuaries Marinespecies Introduced Traits Wiki
What Are Estuaries In Geography Quora
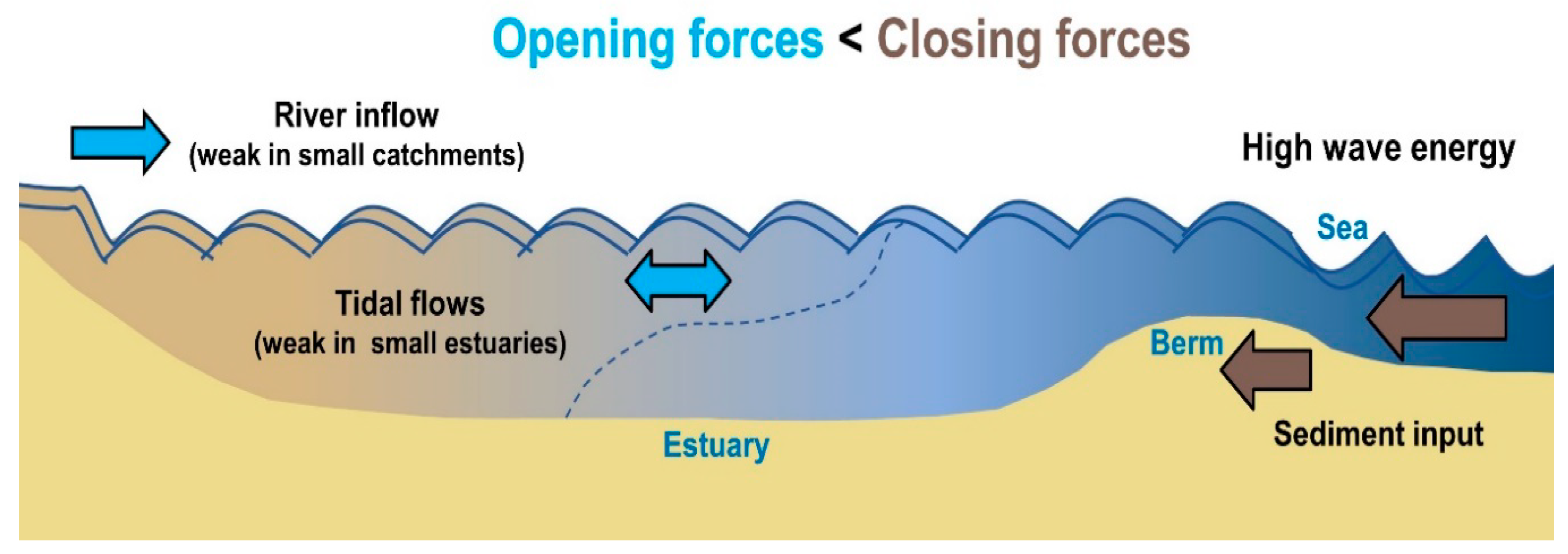
Water Free Full Text Ten Principles To Determine Environmental Flow Requirements For Temporarily Closed Estuaries Html

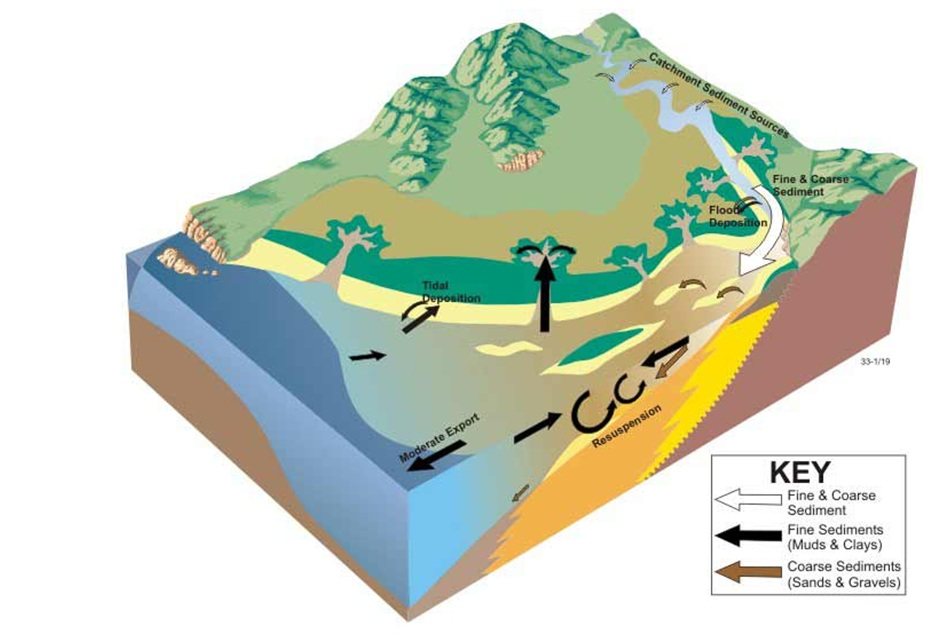
Comments
Post a Comment